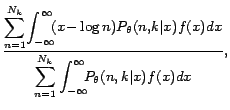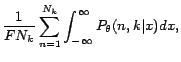�$B Detection of s and
�$B>e$X�(B: Multi-pitch Detection Algorithm
�$BLa$k�(B: Criterion of Model Selection
Detection of the number of speakers
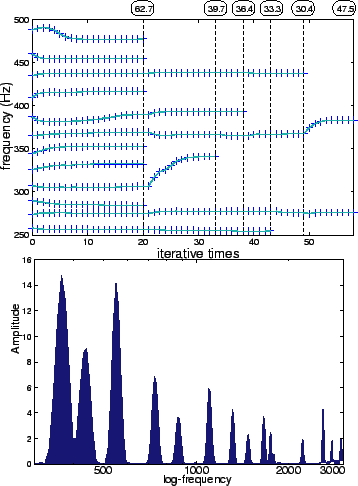
�$B?^�(B 1:
An example of convergence to the true values
�$B?^�(B 2:
Input spectrum for Figure 1
 |
It is generally known that ML estimates obtained by EM algorithm firmly
depend on initial values
and may often converge to undesirable values.
To avoid this, we first prepare extra amount of tied-GMMs in the model
in order to raise possibility of obtaining the true values.
Then, obviously, the model may over-fit the given observed specrum.
If one Gaussian is enough for approximating the shape of one partial,
the same number of underlying harmonic structures must be enough with
the tied-GMMs.
And this number can be detected by reducing tied-GMM one after another
until they become the proper number on the basis of AIC.
The specific operation is as follows:
- Set initial values of
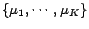 in the limited frequency
range.
in the limited frequency
range.
- Estimate the ML model parameters by EM algorithm. However,
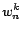 is constrained here as
is constrained here as
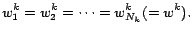 |
|
|
(10) |
This 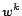 represents the degree of predominance of
represents the degree of predominance of 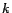 th
tied-GMM.
In Maximization-step, model parameters
th
tied-GMM.
In Maximization-step, model parameters 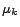 and
and 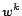 should be
updated to
should be
updated to
where 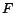 is an integral of
is an integral of 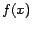 with respect to
with respect to 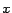 .
.
- Calculate AIC with equation (9). Since there are two free
parameters for each tied-GMM, the model has
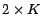 free
parameters altogether. If the AIC increases, the number of
tied-GMMs just before they are reduced in step4 will be the estimate of
the number of harmonic structures.
free
parameters altogether. If the AIC increases, the number of
tied-GMMs just before they are reduced in step4 will be the estimate of
the number of harmonic structures.
- Remove the tied-GMM(s) which conforms either of the two conditions
as below and repeat from step 2.
- The one whose
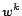 is the minimum among all. Since the
contribution to the maximum log-lik-
is the minimum among all. Since the
contribution to the maximum log-lik-
elihood must be the least.
- The one whose
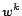 is smaller if the two adjacent
representative means become closer than a certain distance
(threshold). Since the two representative means are presumed to
converge to the same optimal solution.
is smaller if the two adjacent
representative means become closer than a certain distance
(threshold). Since the two representative means are presumed to
converge to the same optimal solution.
An example of how this process actually works is shown in Fig.1 where the
observed spectrum used is depicted in Fig.2.
The broken line represents the point where the model parameters were
judged to be converged and the circled value indicates the value of AIC
at each point. Since AIC takes minimum when 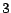 tied-GMMs remain, the
detected number here is
tied-GMMs remain, the
detected number here is 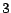 .
.



�$B Detection of s and
�$B>e$X�(B: Multi-pitch Detection Algorithm
�$BLa$k�(B: Criterion of Model Selection
�$BJ?@.�(B16�$BG/�(B3�$B7n�(B25�$BF|�(B